Chemical Structure of NAD+
Research on NAD+
A. Extends Lifespan
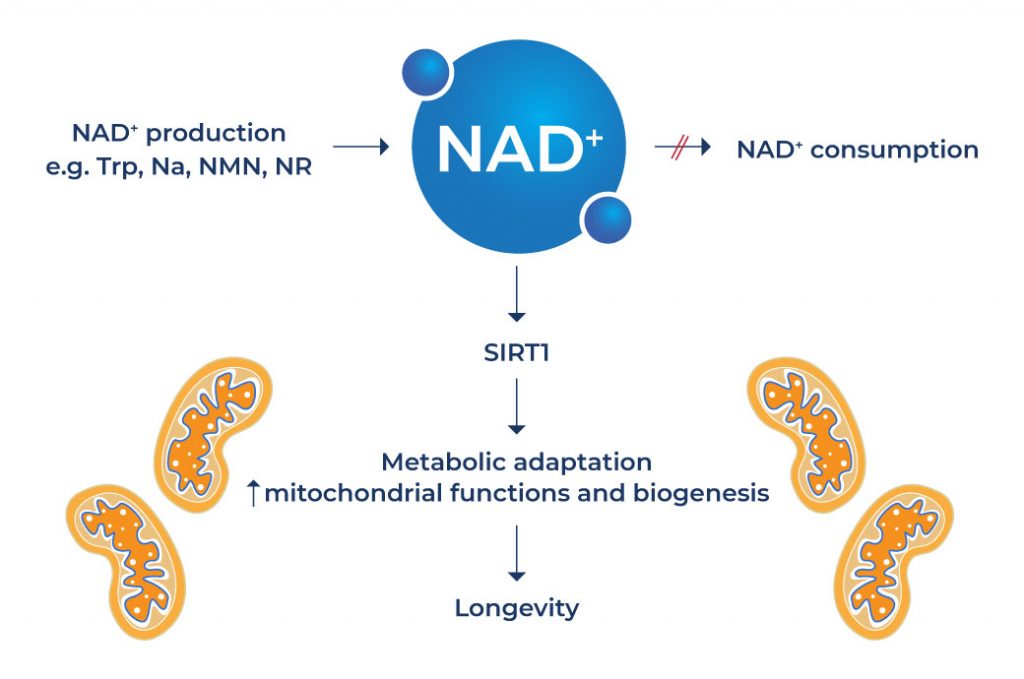
Aging is associated with progressive restriction in the length of telomeres, which are located at chromosome ends. They play an important role in the preservation of chromosome stability. Studies have shown that individuals with longer telomeres have a longer subsequent lifespan. [1-2] Increasing sirtuin activity is known to stabilize telomeres and attenuate age-related telomere shortening. [3] Since NAD+ activates SIRT1, it can help achieve chromosome stability and longer telomeres – all of these mechanisms can increase longevity.
The natural process of aging is associated with a decline in the quality and activity of the “powerhouse of the cell” known as the mitochondria. As the name implies, the mitochondria produce the energy needed to power the cell’s biochemical reactions – everything from the transmission of signals, digestion, muscle function, and other essential bodily processes. Mitochondrial function is a determinant of lifespan and studies show that mitochondrial dysfunction can shorten lifespan. [4-5]
Another mechanism that can help extend lifespan is through the activation of SIRT1 function in the nucleus of cells. Evidence suggests that boosting NAD+ levels through NAD+ supplementation can dramatically ameliorate mitochondrial dysfunction via activation of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1). [6] SIRT1 is an enzyme that plays an integral role in the regulation of proteins involved in cellular metabolism and processes associated with longevity, inflammation, and stress. SIRT1 activation by NAD+ can increase longevity by promoting mitochondrial biogenesis, a cellular process that involves the production of new mitochondria. [7]
A convincing number of evidence suggests that NAD+ can extend lifespan:
- The administration of the NAD+ precursor nicotinamide riboside extended the lifespan of mice without calorie restriction. [8]
- In mice with ataxia-telangiectasia (A-T), a rare disease characterized by progressive neurodegeneration that affects movements and speech, NAD+ replenishment improved lifespan and health span by stimulating neuronal DNA repair and improving mitochondrial quality. [9]
- In a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a medical condition characterized by progressive degeneration of motor neurons, supplementation with a bioavailable NAD+ precursor (nicotinamide riboside, NR) delayed the degeneration of motor neurons, decreased spinal inflammation, and improved survival rate. [10]
- In a mouse model of muscular dystrophy, a condition characterized by gradual weakening of the muscles, treatment with the NAD+ precursor nicotinamide riboside (NR) delayed muscle breakdown and increased lifespan. [11]
- In a mouse model of chronological aging, the administration of CD38 inhibitor 78c increased NAD+ levels which in turn improved exercise performance, endurance, and metabolic function and increased lifespan. [12]
- In Caenorhabditis elegans, a type of worm, NAD+ increased lifespan through the activation of sirtuin (SIR-2). [13-14]
- In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a species of yeast, NAD+ extended the lifespan and ameliorated aging-related conditions. [15]
B. Anti-Aging Benefits
While a decline in the function of the mitochondria has been linked with normal aging, this is also associated with a wide array of age-related medical conditions. Evidence suggests that mitochondrial aging contributes to cellular senescence (also known as biological aging), increased inflammation, decreased stem cell activity, reduced healing rate, and a decline in tissue and organ function. [16] Interestingly, NAD+ can reverse age-related mitochondrial dysfunction via SIRT1 activation.
New research found that some of the age-related changes in the structures of the mitochondria can be reversed through NAD+ supplementation. [17] In this study, the administration of NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide), a molecule that boosts NAD+ levels, via injections in elderly mice reversed age-related mitochondrial deterioration. It was observed that declining NAD+ levels were associated with interruptions in the normal signaling between the cell’s nucleus and mitochondria. Interestingly, raising NAD+ levels restored the communication between these cellular structures.
During the normal process of aging, DNA damage occurs continuously on a massive scale. The age-related DNA damage contributes to cell death and a decline in the function of neurons or nerve cells. This creates a domino effect, causing a gradual decline in a number of bodily functions. NAD+ can mitigate these effects since it is connected to the DNA repair precursor poly adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase 1 (PARP 1). PARP 1 consumes NAD+ in the presence of DNA damage in order to promote cell survival. This in turn can help slow down the effects of aging.
Preclinical evidence also shows that boosting NAD+ levels can help mitigate age-related functional decline:
- In elderly mice, treatment with the NAD+ booster nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) improved blood flow and increased endurance via the promotion of SIRT1-dependent increases in capillary density. [18]
- In mice with progressive weakness and loss of muscle mass, NAD+ repletion improved muscle and mitochondrial function. [19]
- In mice, the administration of the NAD+ booster nicotinamide mononucleotide prevented age-related weight gain and improved physical activity, energy metabolism, lipid profiles, and insulin sensitivity. [20]
- In mouse models of retinal dysfunction, NAD+ deficiency caused metabolic dysfunction in the cells of the retina of the eye, suggesting that restoring NAD+ to youthful levels can help age-related vision loss. [21]
- In mice with mitochondrial dysfunction, oral administration of nicotinamide riboside (NR), a NAD+ precursor, increased mitochondrial numbers and prevented muscle abnormalities. [22]
- In mice, the administration of nicotinamide riboside (NR) prevented noise-induced hearing loss and degeneration of ear cells, suggesting that increasing NAD+ levels can help age-related hearing loss. [23]
- In mice fed with a high-fat diet, the administration of the NAD+ booster nicotinamide mononucleotide prevented diet- and age-induced diabetes by enhancing insulin sensitivity. [24]
C. Increases Energy Levels
NAD+ plays an integral role in energy production and regulation of vital cellular processes. This includes the conversion of food into a usable form of energy called adenosine triphosphate.
Studies suggest that increased ATP production caused by NAD+ may help boost energy levels and reduce fatigue:
- In old mice, supplementation with a NAD+ precursor improved ovarian mitochondrial energy metabolism. [25]
- In obese mice, chronic NAD+ supplementation (1 mg/kg/day for the last 4 weeks) significantly attenuated weight gain and improved diurnal locomotor activity patterns. [26]
- In patients with chronic fatigue syndrome, NAD+ supplementation decreased anxiety and improved heart rate. [27]
- A study reported that NAD+ may be a promising intervention to overcome symptoms of fatigue and to improve the quality of life of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. [28]
- The use of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) plus NAD+ supplementation reduced perceived cognitive fatigue and improved the health-related quality of life in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. [29-31]
- In trained and untrained subjects, NAD+ supplementation was associated with improved exercise endurance. [32]
- 7. NAD+ treatment was found to be more effective than conventional therapy for chronic fatigue syndrome. [33]
D. Promotes Weight Loss
The ability of NAD+ to induce weight loss can be attributed to its energy-boosting mechanisms. With increased energy expenditure, the body will not store additional fat. Instead, the metabolism is increased, resulting in weight loss.
There’s a great deal of evidence supporting the fat-burning effects of NAD+:
- In obese female mice, NAD+ injections reversed glucose intolerance induced by obesity and improved exercise capacity. [34]
- In healthy obese participants, NAD+ supplementation reduced weight by 17.1%. [35]
- In mammalian cells and mouse tissues, NAD+ protected against oxidative stress and high-fat diet-induced metabolic abnormalities. [36]
- In mice, supplementation with NAD+ at 400 mg/kg/day reduced abdominal visceral fat deposition. [37]
- In a study of twins, lower NAD+ levels were associated with acquired obesity. [38]
- A cell study found that NAD+ can promote weight loss by reducing the number of adipocytes (fat cells). [39]
- Several studies have revealed that decreased NAD+ levels in cells were associated with higher fat mass tissues in the skeletal muscles, liver, and brain. [40-43]
- In mice, NAD+ protected against obesity by promoting whole-body energy homeostasis. [44]
- In mice, long-term administration of NAD+ reduced age-associated body weight gain. [45]
- NAD+ supplementation in mice ameliorated maternal obesity. [46]
- A cell study found that NAD+ normalized mitochondrial function and whole-body metabolism. [47]
- In mice fed with a high-fat diet, NAD+ protected against high-fat diet-induced metabolic abnormalities. [48]
E. Increases Muscle Mass and Strength
The anti-aging effects of NAD+ can also help attenuate the age-related decline in muscle mass and strength. Evidence suggests that NAD+ reverses detrimental age-associated changes in muscle by boosting ATP production, increasing mitochondrial function, and reducing inflammation. [49]
Studies show that NAD+ can help combat loss of muscle mass and strength associated with aging and musculoskeletal disease:
- In mice with progressive weakness and loss of muscle mass, NAD+ repletion improved muscle and mitochondrial function. [19]
- In mice with mitochondrial dysfunction, oral administration of nicotinamide riboside (NR), a NAD+ precursor, increased mitochondrial numbers and prevented muscle abnormalities. [22]
- In older men, NAD+ supplementation increased muscle mass and reduced circulating inflammatory cytokines. [50]
- In old mice, restoration of NAD+ levels to normal reversed skeletal muscle aging. [51]
- A 2018 study reported that NAD+ is essential in skeletal muscle development and regeneration. [52]
- In healthy obese men and women, administration of NAD+ at 1g per day for 6 weeks improved skeletal muscle composition. [53]
- A study found that aerobic and resistance exercise training can reverse age-related muscle loss by increasing NAD+ levels. [54]
- In a mouse model of Duchene’s muscular dystrophy (DMD), NAD+ supplementation improved muscle function. [55]
F. Improves Cognitive Function
A decline in NAD+ levels is associated with a number of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and other brain disorders that cause cognitive dysfunction. [11] Interestingly, NAD+ has neuroprotective effects and the ability to decrease the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are linked to a wide array of medical maladies including neurodegenerative diseases.
NAD+ can also help prevent cell death by regulating the activity of polyadenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase 1 (PARP1). [56] PARP1 activity is usually increased in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disease and is associated with increased deposition of abnormal protein structures in the brain. [57] Basically, NAD+ regulates PARP1 activity so that it will not kill too many cells before they can be repaired.
In addition, NAD+ plays important roles in a wide array of biological processes in the brain such as transmission of nerve signals, learning, and memory. [58] NAD+ helps increase the levels of brain chemicals called neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, which are involved in a number of cognitive functions including memory, motivation, attention, mood, and emotions.
A number of strong scientific evidence suggests that NAD+ can help improve cognitive health:
- In a cell study, researchers found that cells treated with NAD+ were more resistant to stress. [59]
- According to a rat study, NAD+ helps protect the brain against oxidative stress. [60]
- A rat udy found that NAD+ can significantly decrease brain injury. [61]
- In a rat study, researchers found that NAD+ is also essential for altering genes that accelerate aging. [62]
- According to a rat study, NAD+ can slow or even reverse the progression of age-related brain diseases. [63]
- Studies found that decreased amounts of NAD+ in the cells accelerate the aging process of the brain. [64-67]
- A rat study found that NAD+ helps the brain function at optimal levels. [68-72]
- Numerous studies suggest that insufficient amounts of NAD+ result in cell breakdown, which in turn accelerates the aging process and causes mitochondrial dysfunction in the brain. [73-77]
- Several studies found that NAD+ is important for the continued production of energy (ATP) by the mitochondria in the brain. [78-81]
- Studies found that NAD+ helps maintain a healthy neurological system and protects against various neurological diseases. [82-84]
- A study found that NAD+ is an essential coenzyme needed for brain function. [85]
- Cell studies found that NAD+ can help improve the functions of the neurons in the brain. [86-88]
- In a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, NAD+ supplementation significantly normalized nerve cell inflammation, synaptic transmission, and DNA damage as well as improved learning, memory, and motor function. [89-95]
- A study found that NAD+ may help improve cognitive function through its anti-inflammatory effects. [96]
G. Fights Cancer
Mitochondrial respiration malfunction and increased glucose uptake are usually observed in cancer cells. Interestingly, increasing NAD+ levels has been shown to boost mitochondrial respiration and reduce glucose (blood sugar) uptake. [97] By counteracting these processes, NAD+ can help prevent the growth of cancer cells.
Increased NAD+ levels can also help boost the activity of SIRT1 and SIRT6, both of which inhibit the growth and spread of tumors via alteration of beta-catenin signaling and reduction of glucose uptake. [98-99]
Studies suggest that NAD+ exerts its anti-cancer effects through several mechanisms:
- A study found that NAD+ regulates cell cycle arrest and programmed cell death of malignant cells. [100]
- In human ovarian tumor tissues, NAD+ enhanced the anti-tumor activities of chemotherapeutic drugs. [101]
- A 2018 study published in Frontiers in Oncology found that NAD+ prevented the progression of cancer by stimulating DNA repair. [102]
- A 2019 study reported that targeting NAD+ metabolism can enhance radiation therapy responses in cancer patients. [103]
- A 2015 study published in the Journal of Molecular & Cellular Oncology found that boosting NAD+ can prevent and treat liver cancer. [104]
H. Improves Cardiovascular Health
NAD+ levels are essential for normal heart function and are associated with improved cardiac recovery from injury. Interestingly, SIRT3, one of the signaling proteins of NAD+, can help improve heart health by preventing enlargement of the heart and scarring. [105-107]
There’s increasing evidence supporting the cardiovascular benefits of NAD+:
- In animal models of heart failure, NAD+ improved a multitude of processes needed for cardiovascular function such as the production of energy for cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells) and reversing vascular dysfunction and oxidative stress. [108-111]
- A cell study reported that NAD+ protected rat heart tissues against apoptosis (programmed cell death). [112]
- In rats with impaired heart function, NAD+ supplementation improved markers of cardiovascular health. [113-116]
- Studies in mice found that NAD+ can stimulate the regeneration of heart muscle cells, reduce left ventricular contractile dysfunction, and prevent heart enlargement. [117-118]
- Rat studies found that higher levels of NAD+ were associated with improved cardiac function. [2, 119]
- Animal studies also found that lower NAD+ levels were associated with mitochondrial dysfunction in heart muscle cells. [120-121]
- A 2015 study published in Nature Reviews found that NAD+ can prevent the progression of obesity through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. [122]
- In patients with heart failure, 5 to 9 days of oral nicotinamide riboside (NR) supplementation increased NAD+ levels, improved respiratory capacity, and decreased proinflammatory cytokines. [123]
- Studies found that increasing NAD+ levels can protect against heart injury caused by insufficient blood supply and pressure overload and can help reduce the size of dead heart tissue. [124-127]
I. Lowers Blood Pressure
NAD+ activates SIRT1 which in turn increases the production of nitric oxide, a substance that helps widen blood vessels to allow an increase in blood flow. This process reduces the pressure within the blood vessels.
A number of studies support the antihypertensive effects of NAD+:
- In healthy middle-aged and older adults, NAD+ supplementation for 6 weeks reduced blood pressure and arterial stiffness. [128]
- A study found that administration of NAD+-boosting molecules decreased blood pressure in Korean subjects. [129]
- In obese men and women, administration of NAD+ at 1-2 g per day for 6-12 weeks significantly reduced blood pressure. [130-131]
J. Improves Blood Sugar Levels
NAD+ can help improve blood sugar levels by reducing glucose (blood sugar) uptake. This in turn prevents sudden spikes in blood sugar which can be detrimental to health. In addition, NAD+ can also help increase the body’s response to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar.
There’s a good deal of evidence supporting the beneficial effects of NAD+ on blood sugar levels:
- In prediabetic women, NAD+ increased muscle insulin sensitivity. [132]
- In obese mice, increased NAD+ levels improved glucose and lipid homeostasis by increasing the activity of SIRT1 and SIRT3. [133-134]
K. Boosts Immune Function
The age-related shortening of telomeres adversely affects the function of the immune system. These adverse changes can significantly increase the risk for severe infection and even death. Studies suggest that patients with significantly shortened telomeres are at higher risk for different medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes mellitus (type 1 and type 2). [135-137] Since NAD+ activates SIRT1, it can help achieve longer and more stable telomeres. This has a positive impact on the overall function of the immune system.
Another mechanism that can help improve the immune function is by suppressing or decreasing the inflammatory response. NAD+ has been shown to possess potent anti-inflammatory properties that can help treat or ward off a broad range of inflammatory conditions.
There is a growing body of evidence that NAD+ can help strengthen immune function:
- Treatment of 24-month-old mice with the NAD+ precursor nicotinamide mononucleotide for 1 week significantly reduced the levels of inflammatory markers such as TNFα and IL-6 in the skeletal muscle. [49]
- Oral nicotinamide has been found to be effective in the management of inflammatory lesions associated with acne vulgaris and acne rosacea. [138]
- In mice with brain inflammation, the administration of a NAD+ precursor attenuated the loss of brain cells and improved behavioral deficits. [139]
- In men exposed to ultraviolet radiation, topical nicotinamide application prevented immunosuppression. [140-142]
- Restoring normal NAD+ levels has been found to decrease the severity of immune reaction in patients with COVID-19 infection. [143]
- Studies suggest that NAD+ has significant immunomodulatory effects such as modulation of cytokine action, regulation of the intercellular adhesion molecules, blockage of mast cell degranulation, and inhibition of protease release from leukocytes. [144-146]
L. Improves Liver Health
By activating SIRT1, NAD+ can produce protective effects on the liver. SIRT1 is known to improve liver health by maintaining mitochondrial integrity, improving cholesterol transport, and improving fatty acid homeostasis. [147-149]
Several lines of evidence suggest that NAD+ can help prevent the development of liver diseases:
- A 2016 study found that NAD+ deficiency in the liver increases the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. [150-151]
- In mice, NAD+ attenuated alcohol-induced liver injury. [152]
- In a mouse model of liver fibrosis, NAD+ prevented liver scarring. [153]
- A 2019 study found that NAD+ protected against aging-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-like liver dysfunction in mice. [154]
- A 2015 study published in Nature Reviews found that NAD+ can prevent the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by influencing the oxidative stress response, programmed cell death, and inflammatory response. [155]
M. Improves Kidney Health
Reduced levels of NAD+ also reduce sirtuin activity. This process is largely responsible for the age-related decline in kidney function.
Latest studies indicate that NAD+ is beneficial for kidney health:
- A 2019 study published in National Reviews in Nephrology found that NAD+ deficiency could lead to chronic kidney disease. [156]
- A 2017 study also found that NAD+ supplementation can help improve kidney function. [157]
- A 2017 study also found that lower NAD+ levels were associated with a higher incidence of acute kidney injury. [158]
- Studies in mice showed that NAD+ protected against kidney injury caused by chemotherapeutic drugs such as cisplatin and other medications that are toxic to the kidneys. [159-165]
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Side Effects
NAD+ side effects are very uncommon. There have been some side effects associated with the use of this drug wherein the patient had one of the issues listed below at some point while being on NAD+. However, these side effects weren’t confirmed to be associated with the treatment and could have been a coincidence and not related to the use of NAD+. Despite this, it was listed as a side effect associated with NAD+ even though these associated side effects are very uncommon.
Side effects associated with NAD+ may include the following:
- Decreased blood levels of phosphorus
- Decreased insulin sensitivity
- Decreased platelets
- Dizziness
- Frontal dull headaches
- Nausea
 The Denim Shop
The Denim Shop
 Japanese Beauty
Japanese Beauty
 European Beauty
European Beauty
 American Beauty
American Beauty
 Makeup
Makeup
 Fragrances
Fragrances
 Bath & Body
Bath & Body
 Hair Care
Hair Care
 Vitamins & Supplements
Vitamins & Supplements
 Home
Home
 Clearance Sale
Clearance Sale